Programmingempire
This article explains how to Find Intersection Using Arrays in C#. Basically, the intersection is a set operation. In general, we compute intersection by taking the common elements from two sets. For instance, consider the following example.
Set A: [6,1,2,3,9,12,5]
Set B: [8,1,2,6,9,12,5,32,67,2]
A ∩ B: [1,2,6,9,12,5]The following code shows how to find intersection using arrays. As can be seen in the code, the maximum number of elements in any set is limited to 10. Therefore, the maximum elements that the resulting array contains are also 10. Although we are implementing this function using arrays, we can also use a variable-length data structure like ArrayList to generalize this function. Besides, the LINQ feature of C#provides the in-built set operations.
The Code to Find Intersection Using Arrays
Since we are using arrays in this example, first we take the size of arrays as input. Further, we create the arrays using that size. After that, we take elements as input from the user. Also, in this example, we sort the input arrays. Now that, we must find the common elements. Hence, the outer for loop takes each element of the second array in each iteration and looks for its match in the first array. As soon as we find a match, we also insert this particular element in the resulting array. Also, increment the index of the output array. Once, the outer for loop completes its execution we get an array with elements common in both arrays.
However, there may be duplicate elements. Therefore, we need to remove duplicates. So, we also need to define a method for duplicate removal. Basically, our duplicate removal function works as follows. It takes each element from the resulting array and checks whether it is already there in the list. In case, the element is not available in the list, it is added to the list. Therefore, the ArrayList contains only unique elements.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace ArrayIntersection
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr3 = new int[10];
int icount;
Console.WriteLine("How many elemts you want in the first array? (must be <=10)");
int size1 = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if(size1>10)
{
Console.WriteLine("Wrong Value!");
Environment.Exit(0);
}
int[] arr1 = new int[size1];
Console.WriteLine("Enter array elements...");
for(int i=0;i<size1;i++)
{
arr1[i] = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
Console.WriteLine("How many elemts you want in the second array? (must be <=10)");
int size2 = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (size2 > 10)
{
Console.WriteLine("Wrong Value!");
Environment.Exit(0);
}
int[] arr2 = new int[size2];
Console.WriteLine("Enter array elements...");
for (int i = 0; i < size2; i++)
{
arr2[i] = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
Array.Sort(arr1);
Array.Sort(arr2);
Console.WriteLine("First Array...");
for(int i=0;i<size1;i++)
Console.Write(arr1[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine("\nSecond Array...");
for (int i = 0; i < size2; i++)
Console.Write(arr2[i] + " ");
icount = 0;
for(int i=0;i<size1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<size2;j++)
{
if(arr1[i]==arr2[j])
{
arr3[icount] = arr1[i];
icount++;
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
for (int i = 0; i < icount; i++)
Console.Write(arr3[i] + " ");
ArrayList mylist = DuplicatesRemove(arr3, icount);
Console.WriteLine("After Removing Duplicates...");
foreach (int x in mylist)
Console.Write(x + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static ArrayList DuplicatesRemove(int[] arr, int c)
{
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++)
{
if (list.IndexOf(arr[i]) == -1)
{
list.Add(arr[i]);
}
}
return list;
}
}
}
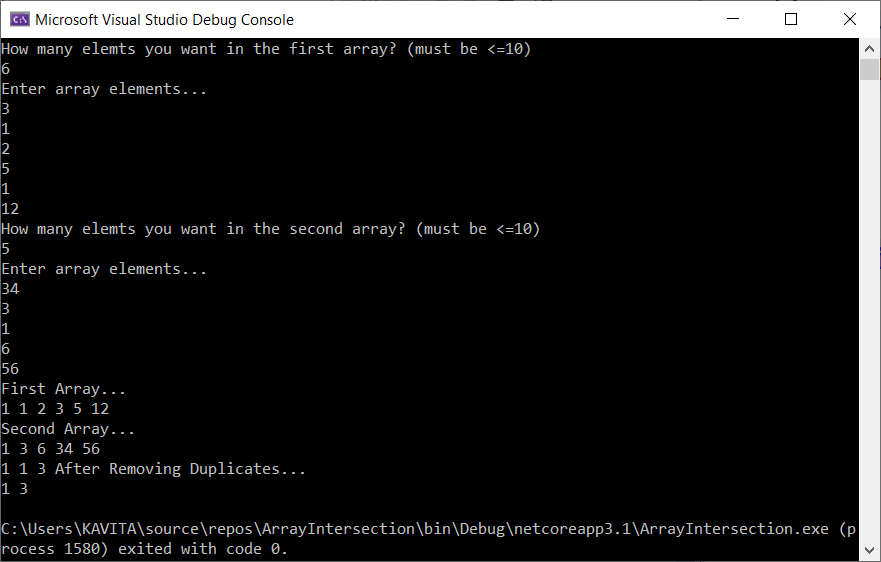
Output
Further Reading
How to Create Instance Variables and Class Variables in Python
Comparing Rows of Two Tables with ADO.NET
Example of Label and Textbox Control in ASP.NET
One Dimensional and Two Dimensuonal Indexers in C#
Private and Static Constructors in C#
Programs to Find Armstrong Numbers in C#
One Dimensional and Two Dimensional Indexers in C#
Generic IList Interface and its Implementation in C#
Creating Navigation Window Application Using WPF in C#
Find Intersection Using Arrays
An array of Objects and Object Initializer
Performing Set Operations in LINQ
Data Binding Using BulletedList Control
Understanding the Quantifiers in LINQ
Deferred Query Execution and Immediate Query Execution in LINQ
Examples of Query Operations using LINQ in C#
An array of Objects and Object Initializer
Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) in C#
Examples of Connected and Disconnected Approach in ADO.NET
IEnumerable and IEnumerator Interfaces
KeyValuePair and its Applications
Learning All Class Members in C#
Examples of Extension Methods in C#
How to Setup a Connection with SQL Server Database in Visual Studio
Understanding the Concept of Nested Classes in C#
A Beginner’s Tutorial on WPF in C#
Explaining C# Records with Examples
Everything about Tuples in C# and When to Use?
Linear Search and Binary search in C#
Examples of Static Constructors in C#
When should We Use Private Constructors?
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET

