Programmingempire
This article explains One Dimensional and Two Dimensional Indexers in C#. In short, an indexer allows an object to behave like an array.
What is an Indexer?
Basically, an indexer is a member of a class in C#. The following list provides important points regarding an indexer.
- Since, indexers are members of a class, they are accessible using the objects of the class.
- Moreover, we can’t use static keyword with indexers. In other words, indexers are instance members.
- We create indexers using this keyword followed by parameters specified in the square brackets.
- Since, we can specify, parameters with indexers, therefore, the indexers can be overloaded.
- Likewise, an indexer can have get and set accessors. Further, at least one of the get or set accessors must be specified. Both accessors can’t be omitted. However, it is valid to specify only get or set accessor.
- Furthermore, it is not possible to specify access modifiers for both accessors. Still we can specify it for any one of the get and set accessor.
- Also, the access modifier for get or set accessor must be more restrictive than the access modifier for the indexer itself. For instance, if the indexer is declared as protected, then get or set accessor can’t be declared as public.
Creating Indexers
To illustrate indexers, consider the following example.
class MyClass
{
int[] a={1,2,3};
//Creating Indexer
public int[int i]
{
get{
return a[i];
}
set{
a[i]=value;
}
}
}The above example demonstrates a simple indexer that we can use to iterate over the array. In general, an indexer has the following syntax.
<access-modifier> <type> this[parameter-list]
{
get{
//statement
}
set{
//statement
}
}
Example Code to Demonstrate One Dimensional and Two Dimensional Indexers in C#
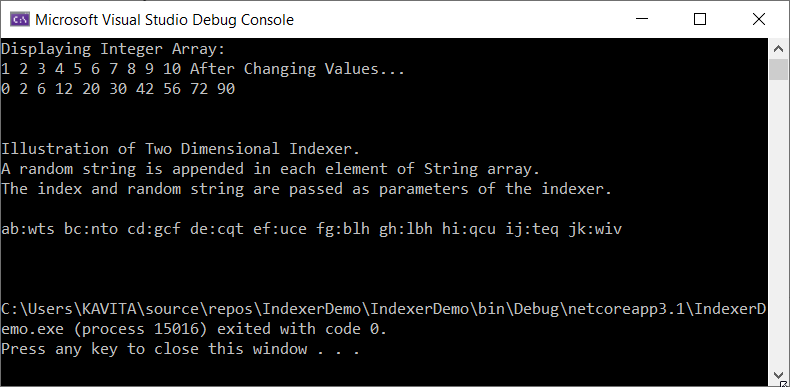
The following program implements One Dimensional and Two Dimensional Indexers in C#. As a matter of fact, when we create an object of the class, we can call the indexer by just using the index with the object name. In order, to call the set accessor we need to assign a value. For example, the statement, ob[i]=10; calls the set accessor. Similarly, for calling the get accessor, we just require to use the object with a specific index in any statement.
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace IndexerDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Demo of One-Dimensional Indexer
MyClass ob = new MyClass();
Console.WriteLine("Displaying Integer Array: ");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
Console.Write(ob[i] + " ");
}
//Set the values using Indexer
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ob[i] = i * (i + 1);
}
Console.WriteLine("After Changing Values...");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.Write(ob[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n\n");
//Demo of Multi-Dimensional Indexer
Console.WriteLine("Illustration of Two Dimensional Indexer.");
Console.WriteLine("A random string is appended in each element of String array.");
Console.WriteLine("The index and random string are passed as parameters of the indexer.\n");
for (int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
//Randomly Generate a String
String s = "";
Random r = new Random();
int n = r.Next(97, 122);
s = s + (char)n;
n = r.Next(97, 122);
s = s + (char)n;
n = r.Next(97, 122);
s = s + (char)n;
//Displaying String array using indexer
Console.Write(ob[i, s] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n\n");
}
}
class MyClass
{
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
String[] sarr = {"ab", "bc", "cd", "de", "ef", "fg", "gh", "hi", "ij", "jk" };
//One-Dimensional Indexer
public int this[int i]
{
get
{
return arr[i];
}
set
{
arr[i] = value;
}
}
//Multi-Dimensional Indexer
public String this[int a, String s]
{
get
{
sarr[a] = String.Join(':', new String[] {sarr[a], s});
return sarr[a];
}
}
}
}
Output
Further Reading
How to Create Instance Variables and Class Variables in Python
Comparing Rows of Two Tables with ADO.NET
Example of Label and Textbox Control in ASP.NET
One Dimensional and Two Dimensuonal Indexers in C#
Private and Static Constructors in C#
Programs to Find Armstrong Numbers in C#
One Dimensional and Two Dimensional Indexers in C#
Generic IList Interface and its Implementation in C#
Creating Navigation Window Application Using WPF in C#
Find Intersection Using Arrays
An array of Objects and Object Initializer
Performing Set Operations in LINQ
Data Binding Using BulletedList Control
Understanding the Quantifiers in LINQ
Deferred Query Execution and Immediate Query Execution in LINQ
Examples of Query Operations using LINQ in C#
An array of Objects and Object Initializer
Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) in C#
Examples of Connected and Disconnected Approach in ADO.NET
IEnumerable and IEnumerator Interfaces
KeyValuePair and its Applications
Learning All Class Members in C#
Examples of Extension Methods in C#
How to Setup a Connection with SQL Server Database in Visual Studio
Understanding the Concept of Nested Classes in C#
A Beginner’s Tutorial on WPF in C#
Explaining C# Records with Examples
Everything about Tuples in C# and When to Use?
Linear Search and Binary search in C#
Examples of Static Constructors in C#
When should We Use Private Constructors?
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
