Programmingempire
This article demonstrates the implementation of Matrix Multiplication in C#. Undeniably, matrix multiplication is one of the most important operations on matrices. By and large matrix multiplication is used in many fields such as computer graphics, scientific computation, implementing algorithms, network theory, data science, applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning, image processing, and so on. Particularly, it is used in many computer graphics tasks such as 2D transformation.
How to Perform Matrix Multiplication?
In order to perform matrix multiplication, we must have two matrices that satisfy the following condition.
Let M1 is a matrix with dimensions, mXn, where m denotes the number of rows, and n denotes the number of columns. Similarly, let M2 is another matrix with dimensions pXq, where p is the number of rows in M2, and q is the number of columns in M2. Further, the condition for matrix multiplication to take place is that n must be equal to q. In other words, the number of columns in the first matrix must be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix.
Afterward, we can specify the matrix multiplication as follows.
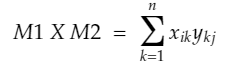
where xik represents the elements in the matrix M1. While ykj denotes the elements in the matrix M2.
Program to Perform Matrix Multiplication in C#
The following program implements matrix multiplication. At first, the program reads the number of rows and columns of the matrices. Further, it checks the condition for valid matrix multiplication. In case, it doesn’t satisfy the necessary condition, the program terminates. Otherwise, it reads the elements of the two matrices. After that, it creates the two-dimensional arrays that hold the matrices and calls the product method.
Accordingly, the product method computes the matrix multiplication using three nested loops. While the innermost loop computes the value of each element in the resulting matrix. In order to do so, it multiplies the corresponding elements in the given row of the first matrix and the corresponding column of the second matrix. Finally, it adds all these values to compute the value of that particular element.
using System;
namespace MatrixProduct
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int m1, n1, m2, n2;
Console.WriteLine("Enter Number of Rows of First Matrix: ");
m1 = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter Number of Columns of First Matrix: ");
n1 = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter Number of Rows of Second Matrix: ");
m2 = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter Number of Columns of Second Matrix: ");
n2 = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if (n1 != m2)
{
Console.WriteLine("Number of Columns of First Matrix is not Equal to the Number of Rows of Second Matrix");
Console.WriteLine("Matrix Multiplication is not Possible!\nExiting....");
Environment.Exit(0);
}
//Declation of 2D array
int[,] mat1 = new int[m1, n1];
int[,] mat2 = new int[m2, n2];
int[,] mat3 = new int[m1, n2];
Console.WriteLine("Enter elements of first matrix: ");
read_matrix(mat1);
Console.WriteLine("Enter elements of second matrix: ");
read_matrix(mat2);
Console.WriteLine("First Matrix (M1): ");
show(mat1);
Console.WriteLine("Second Matrix (M2): ");
show(mat2);
//Find Sum
mat3 = product(mat1, mat2);
Console.WriteLine("Product matrix (M3): ");
show(mat3);
}
public static int[,] product(int[,] a, int[,] b)
{
int m1 = a.GetUpperBound(0) + 1;
int n1 = a.GetUpperBound(1) + 1;
int m2 = b.GetUpperBound(0) + 1;
int n2 = b.GetUpperBound(1) + 1;
int[,] c = new int[m1, n2];
for (int i = 0; i < m1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n2; j++)
{
c[i, j] = 0;
for(int k=0;k<n1;k++)
c[i,j]+=a[i, k] * b[k, j];
}
}
return c;
}
public static void show(int[,] a)
{
for (int i = 0; i < a.GetUpperBound(0) + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < a.GetUpperBound(1) + 1; j++)
{
Console.Write(a[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
public static void read_matrix(int[,] a)
{
for (int i = 0; i < a.GetUpperBound(0) + 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < a.GetUpperBound(1) + 1; j++)
{
a[i, j] = Int32.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
}
}
}
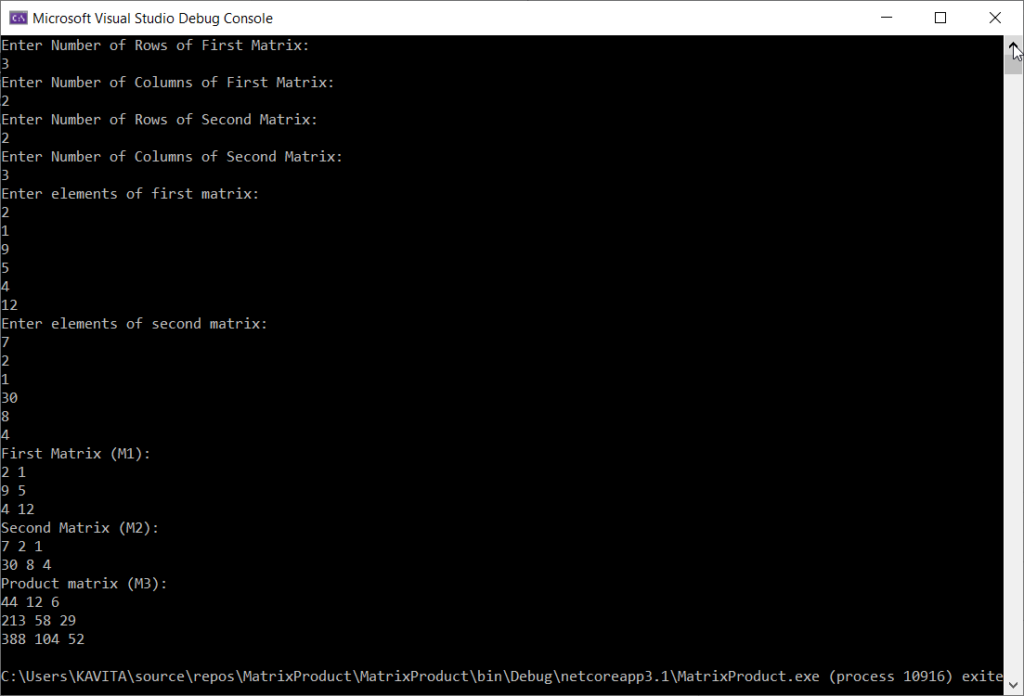
Output
Further Reading
How to Create Instance Variables and Class Variables in Python
Comparing Rows of Two Tables with ADO.NET
Example of Label and Textbox Control in ASP.NET
One Dimensional and Two Dimensuonal Indexers in C#
Private and Static Constructors in C#
Programs to Find Armstrong Numbers in C#
One Dimensional and Two Dimensional Indexers in C#
Generic IList Interface and its Implementation in C#
Creating Navigation Window Application Using WPF in C#
Find Intersection Using Arrays
An array of Objects and Object Initializer
Performing Set Operations in LINQ
Data Binding Using BulletedList Control
Understanding the Quantifiers in LINQ
Deferred Query Execution and Immediate Query Execution in LINQ
Examples of Query Operations using LINQ in C#
An array of Objects and Object Initializer
Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) in C#
Examples of Connected and Disconnected Approach in ADO.NET
IEnumerable and IEnumerator Interfaces
KeyValuePair and its Applications
Learning All Class Members in C#
Examples of Extension Methods in C#
How to Setup a Connection with SQL Server Database in Visual Studio
Understanding the Concept of Nested Classes in C#
A Beginner’s Tutorial on WPF in C#
Explaining C# Records with Examples
Everything about Tuples in C# and When to Use?
Linear Search and Binary search in C#
Examples of Static Constructors in C#
When should We Use Private Constructors?
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
