Programmingempire
In this article I will explain How to Implement Inheritance in Python. In brief, inheritance allows the child class to inherit the properties of the parent class. While the parent class or the base class is the class that is being inherited. While the child class or the subclass is the class that inherits properties from the base class.
Creating the Base Class
We create the base class as an ordinary class containg attributes, methods, and the constructor. The __init__() function is similar to the constructor. Like a C# class constructor, it initializes the state of the object. Also, a python class can use the self keyword that represents the instance of the class. Therefore we can use the self keyword to access the attributes and methods of a class.
While, we can create attributes of a class within the __init__() function. However, we can only use these attributes through the object of that class.
Creating a Subclass in Python
In order to create a subclass in python, we need to enclose the base class name in a parenthesis which follows the subclass name. For example, we can create a subclass as follows:
class subclass_name(baseclass_name):
The following example demonstrates how to create subclasses in python. As can be seen, the class named MyClass is the base class. While, the classes MySubClass1 and MySubClass2 are derived classes. Furter, the base class contains three methods. Also, it has two instance attributes – x, and y.
Using the pass Keyword
Basically, pass represents a null statement in Python. When this statement encounters, nothing happens. The following definition of MySubClass2 indicates that, this class doesn’t add further in its definition.
Overriding Methods in Python
As can be seen in the definition of MyClass and MySubClass2, both of these classes contain the method show(). Therefore, the show() method in MySubClass2 overrides the definition of show() method defined in MyClass.
class MyClass:
def __init__(self, x, y):
print("__init__() Function of Parent Class...")
self.x=x
self.y=y
def showSum(self):
print("Sum = ", self.x+self.y)
def showProduct(self):
print("Product = ", self.x*self.y)
def show(self):
print("x = ", self.x, " y = ", self.y)
class MySubClass1(MyClass):
pass
class MySubClass2(MyClass):
def __init__(self, x, y, z):
super().__init__(x,y)
print("__init__() function of Sub Class 2...")
self.z=z
def ThreeSum(self):
print("Sum of 3 = ", self.x+self.y+self.z)
def ThreeProduct(self):
print("Product of 3 = ", self.x*self.y*self.z)
def show(self):
print("x = ", self.x, " y = ", self.y, " z = ", self.z)
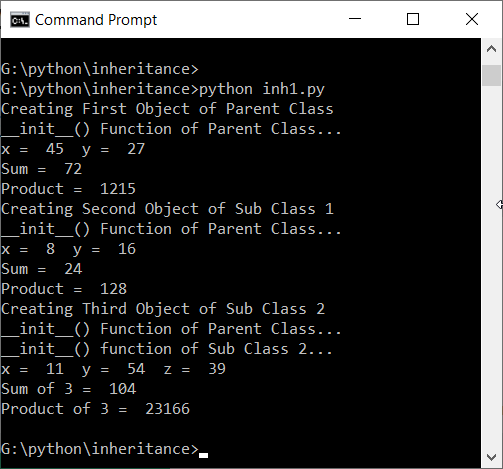
print("Creating First Object of Parent Class")
ob1=MyClass(45, 27)
ob1.show()
ob1.showSum()
ob1.showProduct()
print("Creating Second Object of Sub Class 1")
ob2=MySubClass1(8, 16)
ob2.show()
ob2.showSum()
ob2.showProduct()
print("Creating Third Object of Sub Class 2")
ob3=MySubClass2(11, 54, 39)
ob3.show()
ob3.ThreeSum()
ob3.ThreeProduct()Output
Further Reading
How to Implement Inheritance in Python
Find Prime Numbers in Given Range in Python
Running Instructions in an Interactive Interpreter in Python
Deep Learning Practice Exercise
Deep Learning Methods for Object Detection
Image Contrast Enhancement using Histogram Equalization
Transfer Learning and its Applications
Examples of OpenCV Library in Python
Understanding Blockchain Concepts
Example of Multi-layer Perceptron Classifier in Python
Measuring Performance of Classification using Confusion Matrix
Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Model using Scikit-Learn
Popular Machine Learning Algorithms for Prediction
Long Short Term Memory – An Artificial Recurrent Neural Network Architecture
Python Project Ideas for Undergraduate Students
Creating Basic Charts using Plotly
Visualizing Regression Models with lmplot() and residplot() in Seaborn
Data Visualization with Pandas
A Brief Introduction of Pandas Library in Python
A Brief Tutorial on NumPy in Python
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
