The following code explains How to Use Internal and External JavaScript.
Using Internal JavaScript
<html>
<head>
<title>Using JavaScript</title>
<script>
function change(){
let p=document.getElementById("d1");
p.style.color="#aa6633";
p.style.background="#ffaadd";
p.style.border="#7722aa solid 3px";
p.style.width="40%";
}
function restore(){
let p=document.getElementById("d1");
p.style.color="#3366aa";
p.style.background="#eee";
p.style.border="#111 solid 3px";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<div id="d1" onmouseover="change()" onmouseleave="restore
()">Move the mouse cursor over here!</div>
</center>
</body>
</html>Output
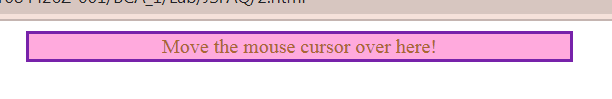
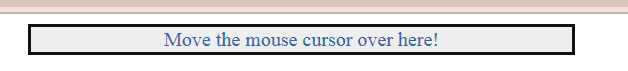
Using External JavaScript
Create a separate file called myfile.js containing the following code.
function change(){
let p=document.getElementById("d1");
p.style.color="#aa6633";
p.style.background="#ffaadd";
p.style.border="#7722aa solid 3px";
p.style.width="40%";
}
function restore(){
let p=document.getElementById("d1");
p.style.color="#3366aa";
p.style.background="#eee";
p.style.border="#111 solid 3px";
}
Include the script tag as follows.
<script src="myfile.js"></script>The complete code is shown below.
<html>
<head>
<title>Using JavaScript</title>
<script src="myfile.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<div id="d1" onmouseover="change()" onmouseleave="restore
()">Move the mouse cursor over here!</div>
</center>
</body>
</html>Further Reading
Evolution of JavaScript from ES1 to ES2020
Introduction to HTML DOM Methods in JavaScript
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
