The following code shows an example to Perform Arithmetic Operations in Java Using switch…Case.
import java.util.*;
class Compute {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, b;
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter First Number: ");
a=Integer.parseInt(s.nextLine());
System.out.println("Enter Second Number: ");
b=Integer.parseInt(s.nextLine());
while(true){
System.out.println("Select an Option...");
System.out.println("1. Add");
System.out.println("2. Subtract");
System.out.println("3. Multiply");
System.out.println("4. Divide");
System.out.println("5. Exit");
System.out.println("Type your selection here: ");
String choice=s.nextLine();
switch(choice){
case "1":
System.out.println("Sum = "+(a+b));
break;
case "2":
System.out.println("Difference = "+(a-b));
break;
case "3":
System.out.println("Product = "+(a*b));
break;
case "4":
System.out.println("Division = "+(a/b));
break;
case "5":
System.exit(0);
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Choice!!");
break;
}
}
}
}Output
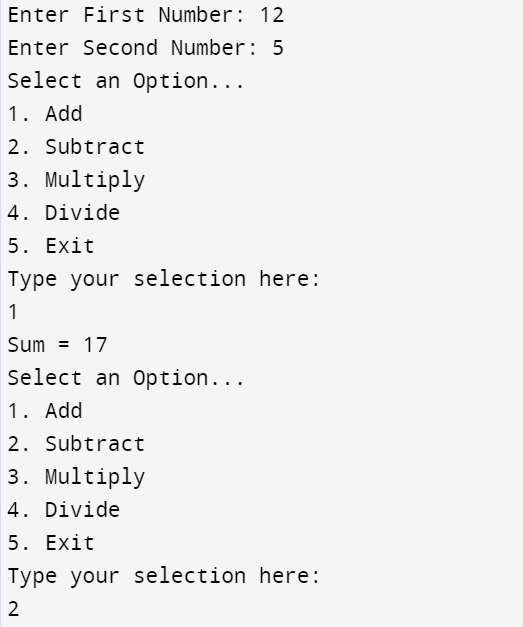
Further Reading
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
