This blog describes how to merge arrays using the spread syntax in ES6.
In ES6, you can merge arrays using the spread syntax (...). The spread syntax allows you to expand elements of an iterable (like an array) into places where multiple elements are expected. For example.
// Arrays to be merged
const array1 = [1, 2, 3];
const array2 = [4, 5, 6];
// Merging arrays using the spread syntax
const mergedArray = [...array1, ...array2];
console.log(mergedArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Output
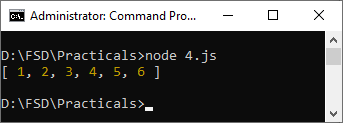
n this example, [...array1, ...array2] is using the spread syntax to merge array1 and array2 into a new array called mergedArray. The spread syntax ...array1 expands the elements of array1, and ...array2 expands the elements of array2, resulting in a single array containing all the elements from both arrays.
You can merge multiple arrays in the same way.
const array1 = [1, 2];
const array2 = [3, 4];
const array3 = [5, 6];
const mergedArray = [...array1, ...array2, ...array3];
console.log(mergedArray); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
This method creates a new array and leaves the original arrays unchanged. If you want to merge arrays without creating a new one, you would need to use methods like push() or concat().
Further Reading
Spring Framework Practice Problems and Their Solutions
From Google to the World: The Story of Go Programming Language
Why Go? Understanding the Advantages of this Emerging Language
Creating and Executing Simple Programs in Go
20+ Interview Questions on Go Programming Language
100+ MCQs On Java Architecture
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
