Programmingempire
In this article, I will provide some Examples of Display and Position Properties in CSS.
Display Property
Basically, the display property determines how the HTML elements will be displayed on a web page. So we can show elements as block-level elements or inline elements using this property. Moreover, it has other values also. According we can have these values for the display property – block, inline, contents, grid, flex, inline-block, inline-flex, inline-grid, list-item, table, table-cell, table-column, table-row, table-caption, table-header-group, table-footer-group, table-row-group, table-column-group, run-in, inline-table, none, initial, and inherit. The following section demonstrates examples of using some of these values for the display property.
Position Property
In order to align HTML elements, we use this property. Accordingly, it takes these values. Further, the examples are shown here.
- static
- absolute
- relative
- fixed
- sticky
- initial
- inherit
Illustrating Examples of Display and Position Properties in CSS
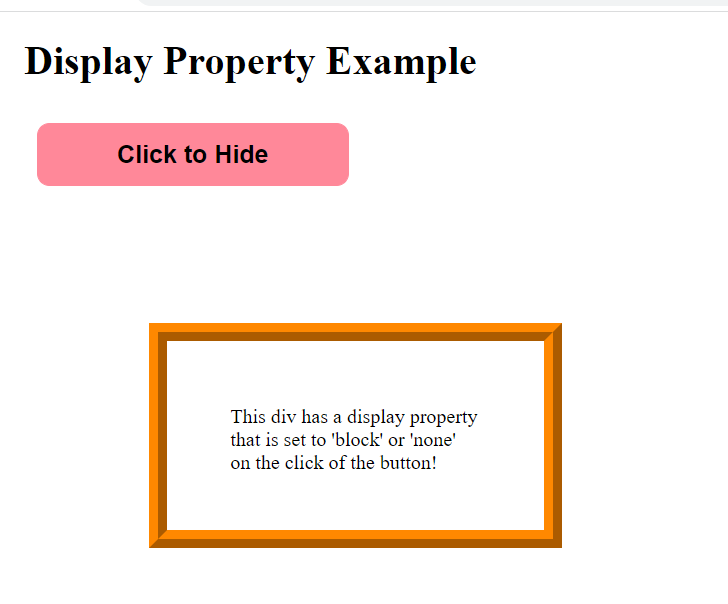
The following example shows how to use display property. while the value none makes the element disappear. Similarly, the value block shows it as a block-level element. The example also shows a button. When the user clicks on the button it runs a function. At first, the javascript function finds the text on the button. For this purpose, it uses the innerHTML property. Meanwhile, it retrieves the button and div by using their id. So, we need to call getElementById() method.
Initially, the button shows ‘Click to Show’ text on it. Also, the Div element is not there. It is because the none value of the display property is specified. Similarly, when the user clicks on the button, the javascript function changes its value to visible. So the div element becomes visible.
<html>
<head>
<title>Display Example</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 20px;
}
.btn{
background: #ff8899;
border: 1px solid #ff8899;
border-radius: 10px;
width: 250px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bolder;
}
.mydiv{
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
border: 15px ridge #ff8800;
margin: 100px;
padding: 50px;
display: none;
}
</style>
<script>
function f1()
{
var x=document.getElementById("b");
var y=document.getElementById("d");
str=x.innerHTML;
if(str=="Click to Show")
{
x.innerHTML="Click to Hide";
y.style.display="block";
}
if(str=="Click to Hide")
{
x.innerHTML="Click to Show";
y.style.display="none";
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Display Property Example</h1>
<button class="btn" id="b" onclick="f1()">Click to Show</button>
<div class="mydiv" id="d">
This div has a display property that is set to 'block' or 'none' on the click of the button!
</div>
</body>
</html>Output
More Examples of Display and Position Properties in CSS
<html>
<head>
<title>Display Example</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 20px;
}
.btn{
background: #ff8899;
border: 1px solid #ff8899;
border-radius: 10px;
width: 250px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bolder;
}
.mydiv{
width: 90px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #ff8800;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
display: inline;
word-wrap: break-word
}
</style>
<script>
function f1()
{
var x=document.getElementById("b");
var y=document.getElementById("d1");
var z=document.getElementById("d2");
var w=document.getElementById("d3");
str=x.innerHTML;
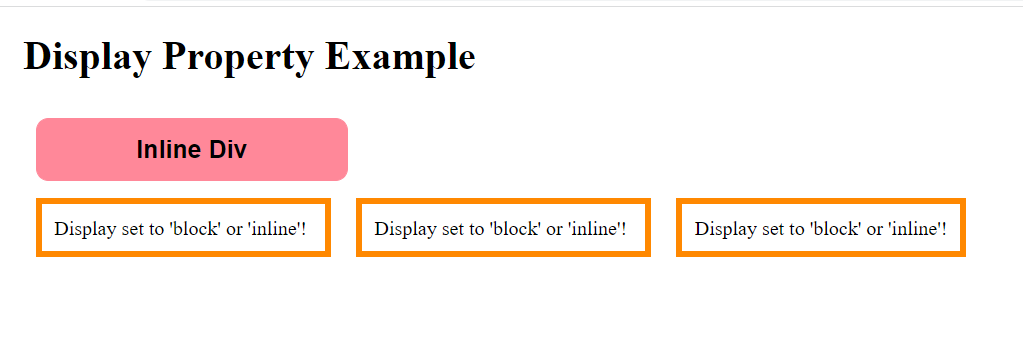
if(str=="Inline Div")
{
x.innerHTML="Block Div";
y.style.display="block";
z.style.display="block";
w.style.display="block";
}
if(str=="Block Div")
{
x.innerHTML="Inline Div";
y.style.display="inline";
z.style.display="inline";
w.style.display="inline";
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Display Property Example</h1>
<button class="btn" id="b" onclick="f1()">Inline Div</button><br/><br/>
<div class="mydiv" id="d1">
Display set to 'block' or 'inline'!
</div>
<div class="mydiv" id="d2">
Display set to 'block' or 'inline'!
</div>
<div class="mydiv" id="d3">
Display set to 'block' or 'inline'!
</div>
</body>
</html>Output
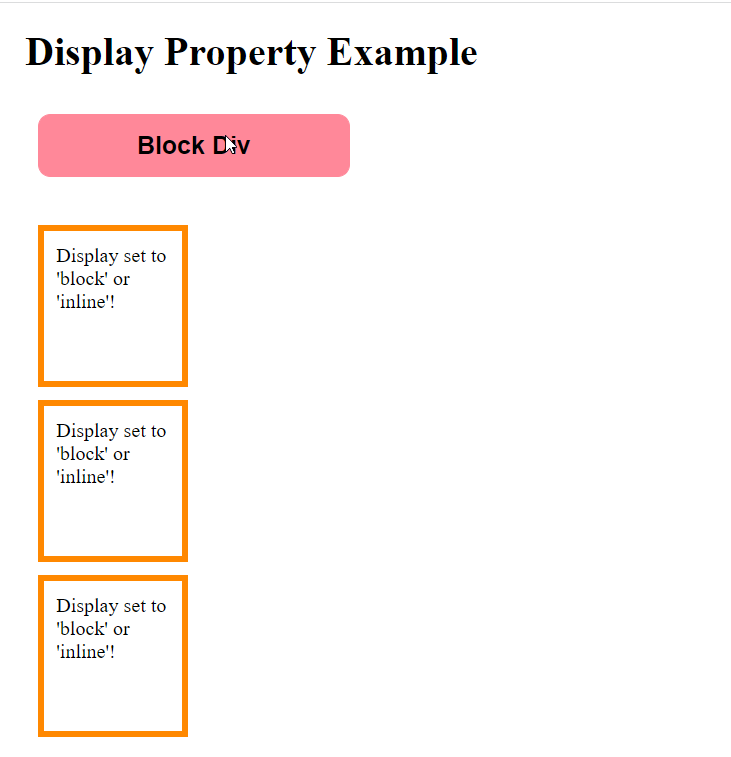
As shown above elements are displayed as block elements.
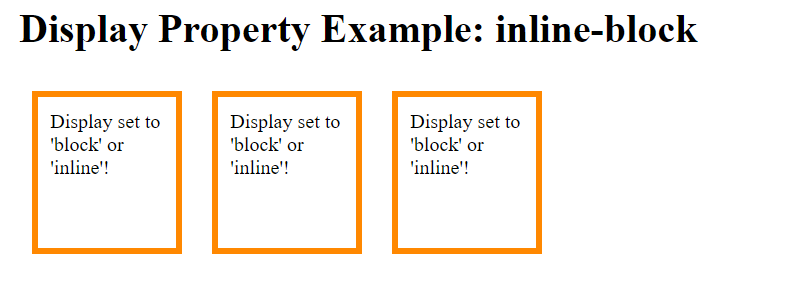
Display: inline-block
For the purpose of showing elements as inline-level block containers we use the property value inline-block.
<html>
<head>
<title>Display Example</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 20px;
}
.btn{
background: #ff8899;
border: 1px solid #ff8899;
border-radius: 10px;
width: 250px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bolder;
}
.mydiv{
width: 90px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #ff8800;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
display: inline-block;
word-wrap: break-word
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Display Property Example: inline-block</h1>
<div class="mydiv">
Display set to 'block' or 'inline'!
</div>
<div class="mydiv">
Display set to 'block' or 'inline'!
</div>
<div class="mydiv">
Display set to 'block' or 'inline'!
</div>
</body>
</html>Output
Example of display: list-item
In order to display the elements as <li> elements, we use the list-item value of the display property. The following figure shows it.

Example of display:content
In case we don’t want to show the container, we can use the contents value for display property. As a result, container will disappear and only the content remains.
<html>
<head>
<title>Display Example</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 20px;
}
.btn{
background: #ff8899;
border: 1px solid #ff8899;
border-radius: 10px;
width: 250px;
height: 50px;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bolder;
}
.mydiv{
width: 90px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #ff8800;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
display: contents;
word-wrap: break-word
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Display Property Example: contents</h1>
<div class="mydiv">
Display set to 'content'!
</div>
<div class="mydiv">
Display set to 'content'!
</div>
<div class="mydiv">
Display set to 'content'!
</div>
</body>
</html>Output
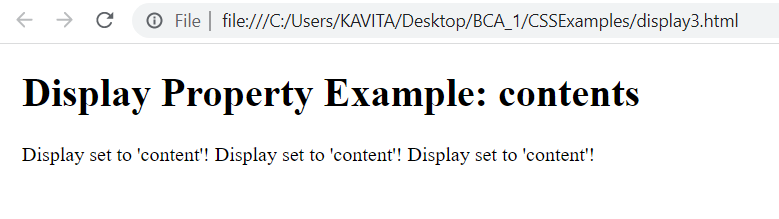
Eample of display:content
Another value for display property is table-cell. When we use this value, the element behaves as table cell like <td>. So we use display: table-cell in the above example to get the following output.
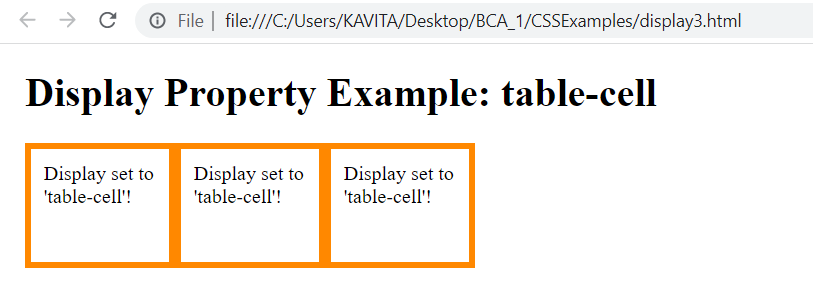
The following code shows Examples of Display and Position Properties in CSS
As can be seen in the code, the position is set to fixed. Also, the display is block. Further, left and top properties indicate position of each div. When user scrolls, the postion of each div remains fixed.
<html>
<head>
<title>Display Example</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 20px;
}
.mydiv{
width: 90px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #ff8800;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
display: block;
word-wrap: break-word
}
.mydiv1{
position: fixed;
top: 0; left:0;
}
.mydiv2{
position: fixed;
top: 0; left:100;
}
.mydiv3{
position: fixed;
top: 0; left:200;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Display: block and Position: sticky</h1>
<div class="mydiv mydiv1">
First Div
</div>
<div class="mydiv mydiv2">
Second Div
</div>
<div class="mydiv mydiv3">
Third Div
</div>
<div style="height: 1000px; background: #cdcdcd; width: 100%;"></div>
</body>
</html>Output
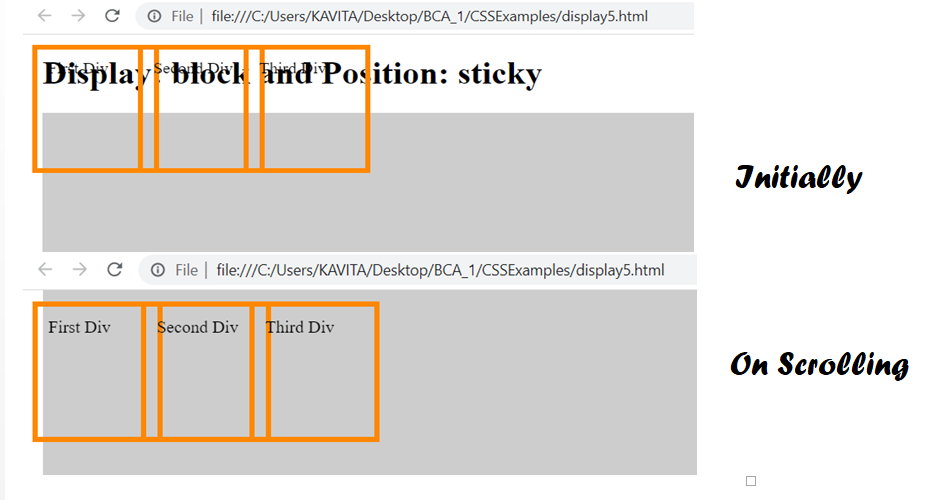
More Examples of Display and Position Properties in CSS
The following code shows value of display is block. Also, the position of each div is sticky.
<html>
<head>
<title>Display Example</title>
<style>
body{
margin: 20px;
}
.mydiv{
width: 90px;
height: 100px;
border: 5px solid #ff8800;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
display: block;
word-wrap: break-word
}
.mydiv1{
position: sticky;
top: 0; left:0;
}
.mydiv2{
position: sticky;
top: 0; left:100;
}
.mydiv3{
position: sticky;
top: 0; left:200;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Display: block and Position: sticky</h1>
<div class="mydiv mydiv1">
First Div
</div>
<div class="mydiv mydiv2">
Second Div
</div>
<div class="mydiv mydiv3">
Third Div
</div>
<div style="height: 1000px; background: #cdcdcd; width: 100%;"></div>
</body>
</html>Output
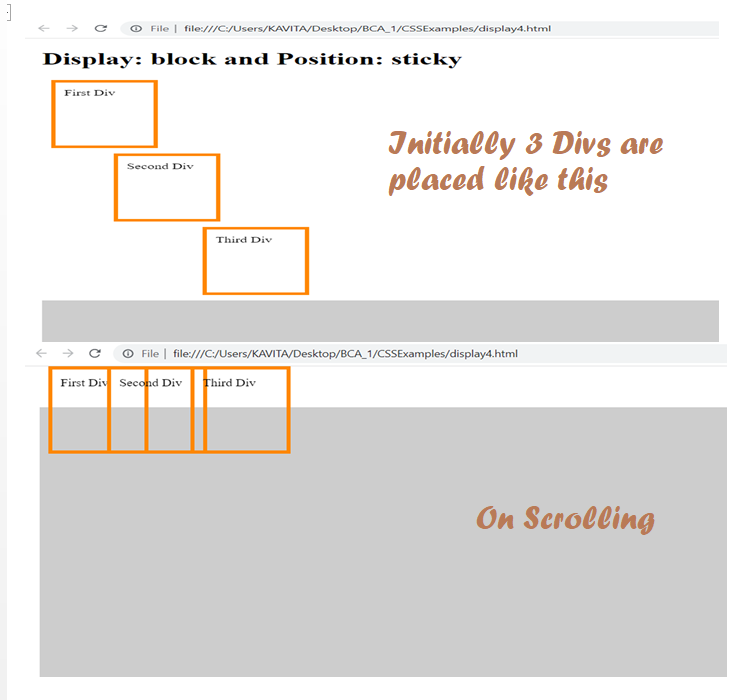
Further Reading
Example of Column Properties in CSS
Examples of Outline Properties in CSS
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
