Programmingempire
This article demonstrates a Database Record Navigation Example Using ADO.NET. The following example uses VB.NET. While the C# code is available here. Basically, .NET Framework provides the ADO.NET library that comprises classes and methods for connecting the application with a database and performing various operations on it.
Creating Database in SQL Server
At first, start Visual Studio and create a Windows Forms application in VB.NET. The following application is created using Visual Studio 2019.
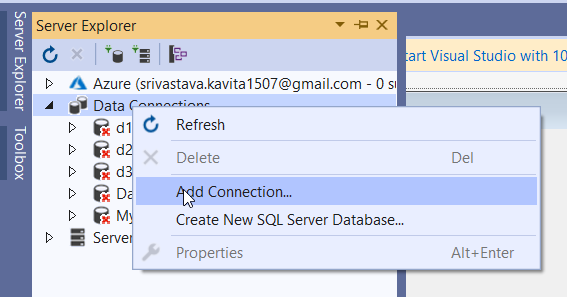
Once, the application is created, select Server Explorer from the View menu. Now click on the Server Explorer and then right-click on the Add Connection option. The following figure demonstrates it.
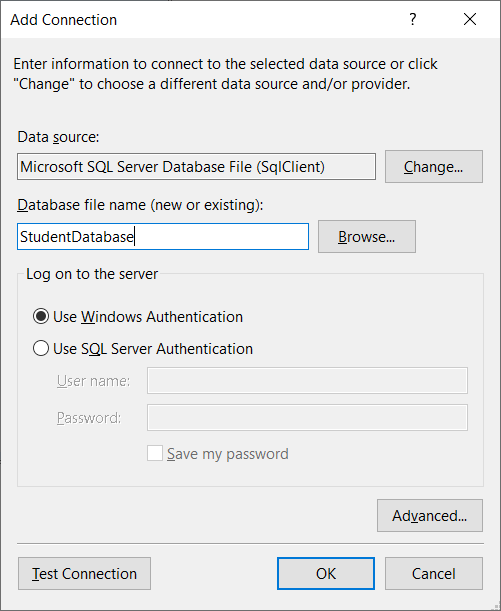
After that, specify the name of the database and click on OK as the following figure shows.
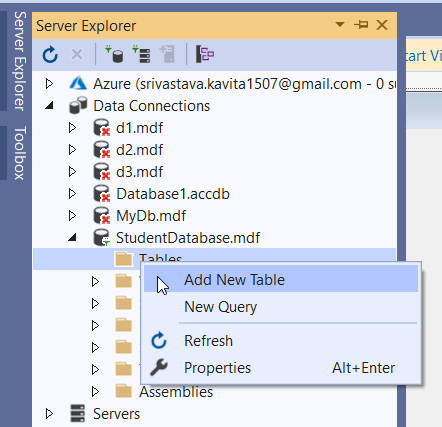
If the database doesn’t exist, click on the “Yes” option to create it. Now the database is visible in the Server Explorer. Further, expand the database and click on the Tables folder. After that right-click on the Add New Table option. The following figure demonstrates it.
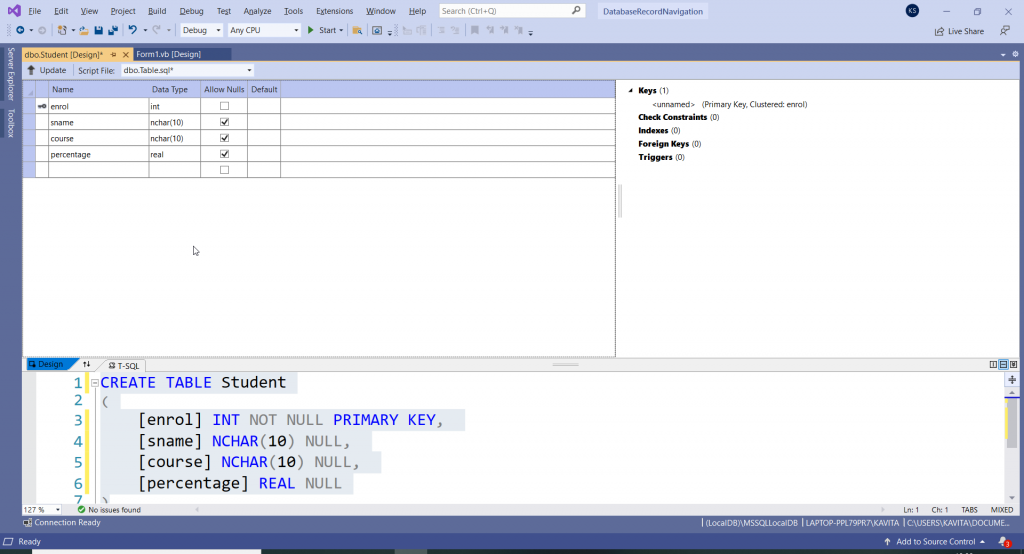
Further, create a new table as shown in the figure.
Now click on the Update button and then click on the Update Database. When you click on the Refresh option in the Server Explorer, the database table becomes visible as shown below.
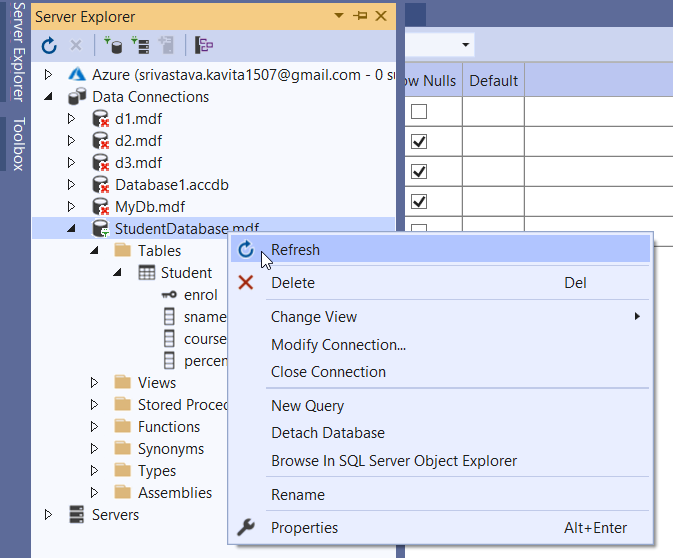
Creating a Database Table
After that right-click on the Student table and select the option Show Table Data. The following figure shows it.
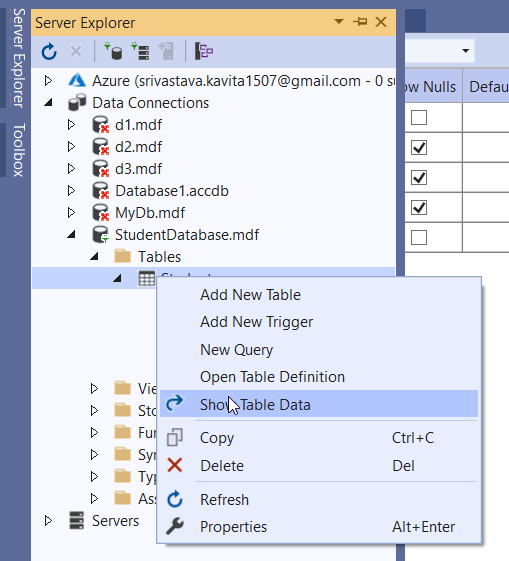
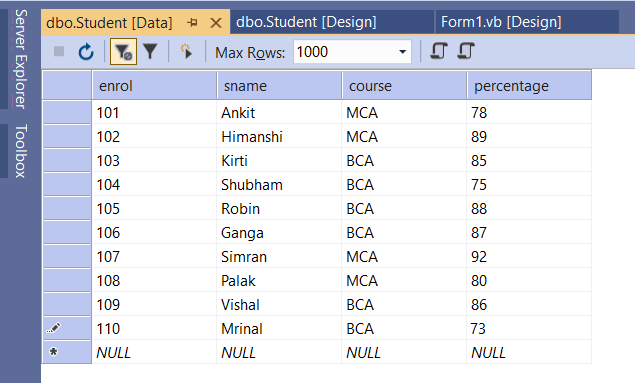
Once the database table opens, add some records, save the table data and close it.
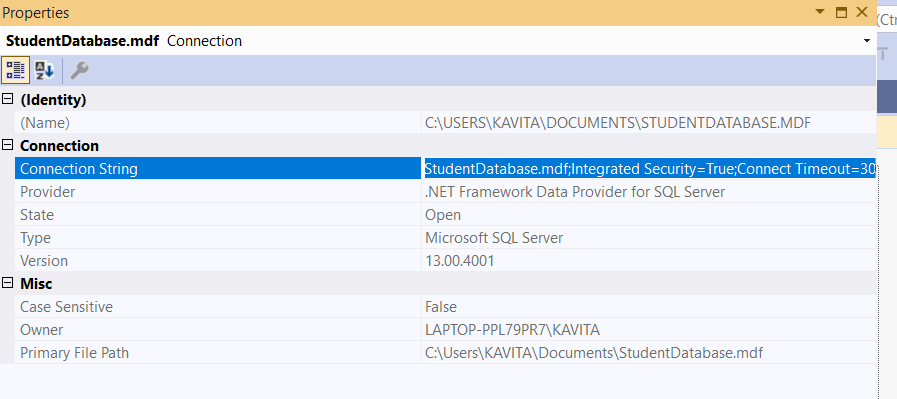
Further, right-click on the database in Server Explorer and click on the Properties option as shown below.
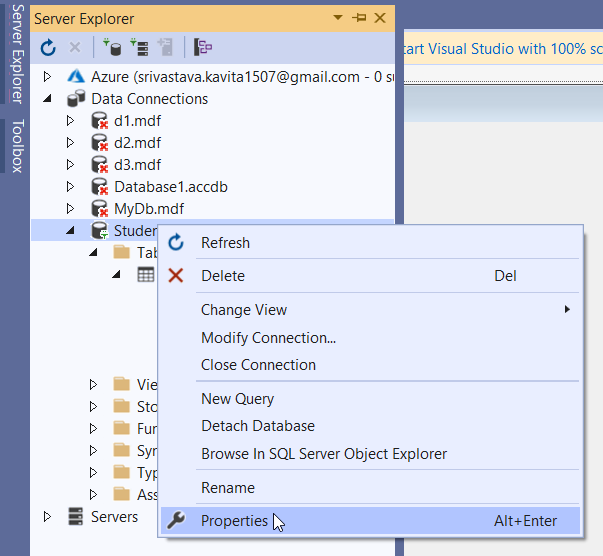
Now select the value of the Connection String property and copy it. When we create a Connection object, we need to specify the connection string. Therefore, we will use the value of the connection string in the code.
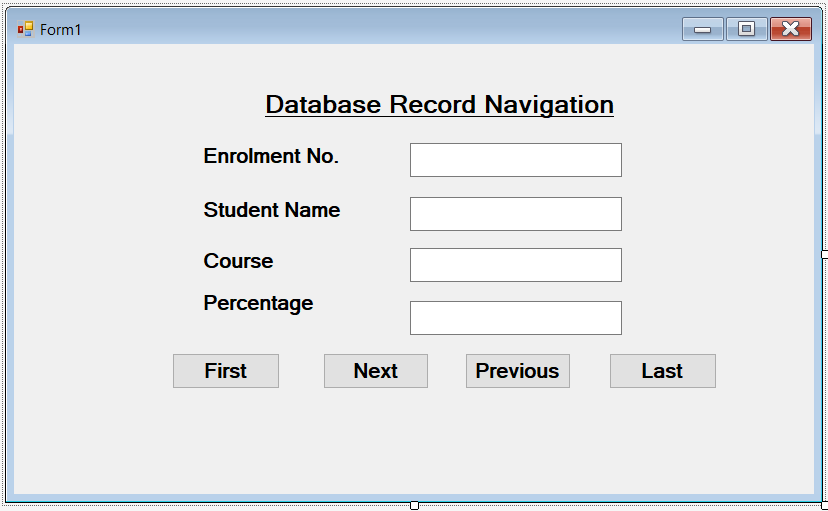
Design a Form for Database Record Navigation Example
Once our database is ready, we can develop the application. Therefore, we can start with the Form Design. The following figure shows the Form for Database Record Navigation Example.
Complete Code
After that, click on the form and write the code for connecting with the database and the corresponding buttons.
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Data.SqlClient
Public Class Form1
Dim con As SqlConnection
Dim da As SqlDataAdapter
Dim ds As DataSet
Dim i As Integer = 0
Dim n As Integer
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
con = New SqlConnection("Data Source=(LocalDB)\MSSQLLocalDB;AttachDbFilename=C:\Users\KAVITA\Documents\StudentDatabase.mdf;Integrated Security=True;Connect Timeout=30")
con.Open()
da = New SqlDataAdapter("select * from Student", con)
ds = New DataSet()
da.Fill(ds, "Student")
n = ds.Tables("Student").Rows.Count
Dim dr As DataRow
dr = ds.Tables("Student").Rows(0)
TextBox1.Text = dr(0).ToString
TextBox2.Text = dr(1).ToString
TextBox3.Text = dr(2).ToString
TextBox4.Text = dr(3).ToString
End Sub
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
Dim dr As DataRow
dr = ds.Tables("Student").Rows(0)
TextBox1.Text = dr(0).ToString
TextBox2.Text = dr(1).ToString
TextBox3.Text = dr(2).ToString
TextBox4.Text = dr(3).ToString
End Sub
Private Sub Button4_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button4.Click
Dim dr As DataRow
dr = ds.Tables("Student").Rows(n - 1)
TextBox1.Text = dr(0).ToString
TextBox2.Text = dr(1).ToString
TextBox3.Text = dr(2).ToString
TextBox4.Text = dr(3).ToString
End Sub
Private Sub Button2_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button2.Click
Dim dr As DataRow
If (i = n - 1) Then
Button4.PerformClick()
Else
i = i + 1
dr = ds.Tables("Student").Rows(i)
TextBox1.Text = dr(0).ToString
TextBox2.Text = dr(1).ToString
TextBox3.Text = dr(2).ToString
TextBox4.Text = dr(3).ToString
End If
End Sub
Private Sub Button3_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button3.Click
Dim dr As DataRow
If (i = 0) Then
Button1.PerformClick()
Else
i = i - 1
dr = ds.Tables("Student").Rows(i)
TextBox1.Text = dr(0).ToString
TextBox2.Text = dr(1).ToString
TextBox3.Text = dr(2).ToString
TextBox4.Text = dr(3).ToString
End If
End Sub
End Class
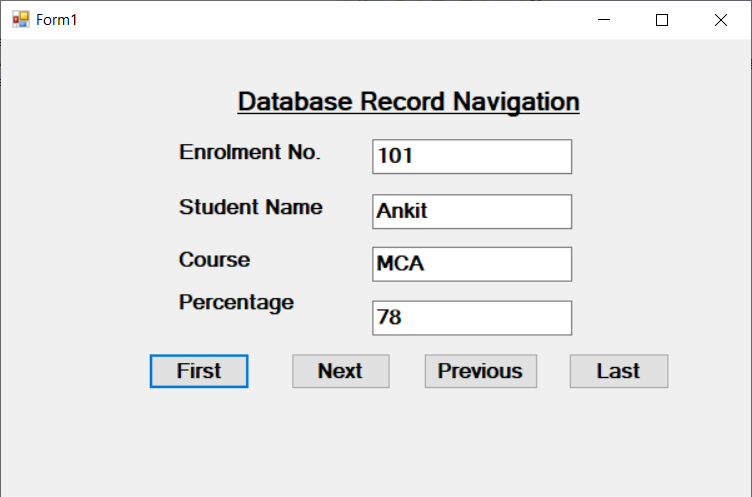
Output
- Angular
- ASP.NET
- C
- C#
- C++
- CSS
- Dot Net Framework
- HTML
- IoT
- Java
- JavaScript
- Kotlin
- PHP
- Power Bi
- Python
- Scratch 3.0
- TypeScript
- VB.NET
